WordPressで作成した複数のサイトを10年ほど運用しています。
いつもレンタルサーバーが提供するWordPress簡単インストールを使ってインストールして無料テンプレートを使ってサイト作成 運用を行ってきました。
頭の中ではWordPressの仕組みを理解したいと思いつつ、サイト運用に入るとコンテンツ作成とSEO施策に時間を取られWordPressの本質を理解しないまま時間がたってしまいました。
この度、「WordPressはどうやって動き始めるのだろう」ということがどうしても気になり頭から離れなくなったので時間をとり調べてみることにしました。
WordPressの作り
いま現在、WordPress について分かっているイメージは、下記の通りです。
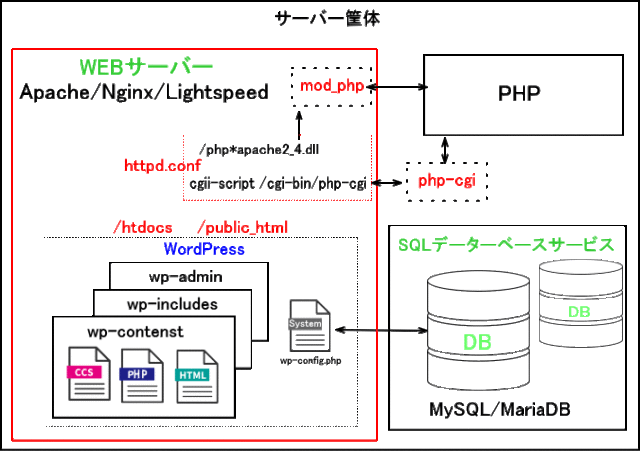
稼働環境:
LAMP(「Linux」「Apache」「MySQL」「PHP」)
LEMP(「Linux」「Nginx」「MySQL」「PHP」)
L?MP(「Linux」「LiteSpeed」「MySQL」「PHP」)
WordPressファイル構成:
WordPressを構成する3つのフォルダー【※3】参照。
PHP:
モジュール版は、WEBサーバーの拡張モジュールの一つとして実行される。
CGI版は、WEBサーバーとは別のプロセスとして実行される。
WordPressの起動
以下にWEBサーバーがApacheの場合について記載していきます。
公開フォルダのindex.phpが実行される~①
ワードプレスを公開フォルダ/htdocs配下のサブフォルダー/wordpressにインストールしているので、公開フォルダindex.phpを下記の通りに変更して、/htdoc/wordpressフォルダーへ制御が渡るようにする。
header('Location: '.$uri.'/htdocs/'); を以下に変更する。
header('Location: '.$uri.'/wordpress/')
<?php
if (!empty($_SERVER['HTTPS']) && ('on' == $_SERVER['HTTPS'])) {
$uri = 'https://';
} else {
$uri = 'http://';
}
$uri .= $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'];
header('Location: '.$uri.'/wordpress/');
exit;
?>
Something is wrong with the XAMPP installation :-(ワードプレスインストール/docs/wordpressの.htaccessでリダイレクト
.htaccessの設定により、すべてのアクセスがindex.phpにリダイレクトされて実行される。
# BEGIN WordPress
# "BEGIN WordPress" から "END WordPress" までのディレクティブ (行) は
# 動的に生成され、WordPress フィルターによってのみ修正が可能です。
# これらのマーカー間にあるディレクティブへのいかなる変更も上書きされてしまいます。
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule .* - [E=HTTP_AUTHORIZATION:%{HTTP:Authorization}]
RewriteBase /wordpress/
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /wordpress/index.php [L]
</IfModule>wp-blog-header.phpを呼び出す。
index.php内で、WordPress関数wp-blog-header.phpを呼び出す。
<?php
/**
* Front to the WordPress application. This file doesn't do anything, but loads
* wp-blog-header.php which does and tells WordPress to load the theme.
*
* @package WordPress
*/
/**
* Tells WordPress to load the WordPress theme and output it.
*
* @var bool
*/
define( 'WP_USE_THEMES', true );
/** Loads the WordPress Environment and Template */
require __DIR__ . '/wp-blog-header.php';wp-blog-header.phpに関して
wp-blog-header.phpの働き
$wp_query オブジェクトに現在のリクエストを定義する情報を与える。
Codex 関数リファレンス/WP Query
$wp_query はどのタイプのクエリを扱っているのか (カテゴリーアーカイブ、年月別アーカイブ、フィード、検索など) を確定し、要求された投稿を取り出せる。
$wp_query はリクエスト上の情報を多く保持し後からでも利用することができます。
<?php
/**
* Loads the WordPress environment and template.
*
* @package WordPress
*/
if ( ! isset( $wp_did_header ) ) {
$wp_did_header = true;
// ① Load the WordPress library.
require_once __DIR__ . '/wp-load.php';
// ② Set up the WordPress query.
wp();
// ③Load the theme template.
require_once ABSPATH . WPINC . '/template-loader.php';
}wp-blog-header.phpの動き
① wp-load.phpを呼び出す
:ワードプレスライブラリを読み込む。
(wp-confing.phpの設定を読み込む。)
② wp();の実行
機能:Set up the WordPress query.
(アクセスされた URL に該当するページのデータをデータベースから読み込む。)
【参考】wp( )仕様(リンク先 Codex関数リファレンス/WP Query)
③ template-loader.phpを呼び出す。
(リクエスト内容に応じて読み込むテンプレートを選択し表示する。【テンプレートロード階層】)
【参考】テンプレート階層(リンク先 WordPressドキュメント)
wp-load.phpの動き
wp-confing.phpが存在する場合設定を読み込みます。
(require_once ABSPATH . 'wp-config.php';)
wp-confing.phpは、自身のファイルの最後でwp-settings.phpを呼び込みWordPressの環境設定を行います。
(require_once(ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php');)
<?php
/**
* Bootstrap file for setting the ABSPATH constant
* and loading the wp-config.php file. The wp-config.php
* file will then load the wp-settings.php file, which
* will then set up the WordPress environment.
*
* If the wp-config.php file is not found then an error
* will be displayed asking the visitor to set up the
* wp-config.php file.
*
* Will also search for wp-config.php in WordPress' parent
* directory to allow the WordPress directory to remain
* untouched.
*
* @package WordPress
*/
/** Define ABSPATH as this file's directory */
if ( ! defined( 'ABSPATH' ) ) {
define( 'ABSPATH', __DIR__ . '/' );
}
/*
* The error_reporting() function can be disabled in php.ini. On systems where that is the case,
* it's best to add a dummy function to the wp-config.php file, but as this call to the function
* is run prior to wp-config.php loading, it is wrapped in a function_exists() check.
*/
if ( function_exists( 'error_reporting' ) ) {
/*
* Initialize error reporting to a known set of levels.
*
* This will be adapted in wp_debug_mode() located in wp-includes/load.php based on WP_DEBUG.
* @see http://php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.constants.php List of known error levels.
*/
error_reporting( E_CORE_ERROR | E_CORE_WARNING | E_COMPILE_ERROR | E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE | E_USER_ERROR | E_USER_WARNING | E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR );
}
/*
* If wp-config.php exists in the WordPress root, or if it exists in the root and wp-settings.php
* doesn't, load wp-config.php. The secondary check for wp-settings.php has the added benefit
* of avoiding cases where the current directory is a nested installation, e.g. / is WordPress(a)
* and /blog/ is WordPress(b).
*
* If neither set of conditions is true, initiate loading the setup process.
*/
if ( file_exists( ABSPATH . 'wp-config.php' ) ) {
/** The config file resides in ABSPATH */
require_once ABSPATH . 'wp-config.php';
} elseif ( @file_exists( dirname( ABSPATH ) . '/wp-config.php' ) && ! @file_exists( dirname( ABSPATH ) . '/wp-settings.php' ) ) {
/** The config file resides one level above ABSPATH but is not part of another installation */
require_once dirname( ABSPATH ) . '/wp-config.php';
} else {
// A config file doesn't exist.
define( 'WPINC', 'wp-includes' );
require_once ABSPATH . WPINC . '/load.php';
// Standardize $_SERVER variables across setups.
wp_fix_server_vars();
require_once ABSPATH . WPINC . '/functions.php';
$path = wp_guess_url() . '/wp-admin/setup-config.php';
/*
* We're going to redirect to setup-config.php. While this shouldn't result
* in an infinite loop, that's a silly thing to assume, don't you think? If
* we're traveling in circles, our last-ditch effort is "Need more help?"
*/
if ( false === strpos( $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'], 'setup-config' ) ) {
header( 'Location: ' . $path );
exit;
}
define( 'WP_CONTENT_DIR', ABSPATH . 'wp-content' );
require_once ABSPATH . WPINC . '/version.php';
wp_check_php_mysql_versions();
wp_load_translations_early();
// Die with an error message.
$die = '<p>' . sprintf(
/* translators: %s: wp-config.php */
__( "There doesn't seem to be a %s file. I need this before we can get started." ),
'<code>wp-config.php</code>'
) . '</p>';
$die .= '<p>' . sprintf(
/* translators: 1: Documentation URL, 2: wp-config.php */
__( 'Need more help? <a href="%1$s">Read the support article on %2$s</a>.' ),
__( 'https://wordpress.org/support/article/editing-wp-config-php/' ),
'<code>wp-config.php</code>'
) . '</p>';
$die .= '<p>' . sprintf(
/* translators: %s: wp-config.php */
__( "You can create a %s file through a web interface, but this doesn't work for all server setups. The safest way is to manually create the file." ),
'<code>wp-config.php</code>'
) . '</p>';
$die .= '<p><a href="' . $path . '" class="button button-large">' . __( 'Create a Configuration File' ) . '</a></p>';
wp_die( $die, __( 'WordPress › Error' ) );
}wp-config.php
DB情報、認証用ユニークキー設定後wp-settings.phpを呼び出す。
/**
* WordPress データベーステーブルの接頭辞
*
* それぞれにユニーク (一意) な接頭辞を与えることで一つのデータベースに複数の WordPress を
* インストールすることができます。半角英数字と下線のみを使用してください。
*/
$table_prefix = 'wp4_';
/**
* 開発者へ: WordPress デバッグモード
*
* この値を true にすると、開発中に注意 (notice) を表示します。
* テーマおよびプラグインの開発者には、その開発環境においてこの WP_DEBUG を使用することを強く推奨します。
*
* その他のデバッグに利用できる定数については Codex をご覧ください。
*
* @link http://wpdocs.osdn.jp/WordPress%E3%81%A7%E3%81%AE%E3%83%87%E3%83%90%E3%83%83%E3%82%B0
*/
define('WP_DEBUG', false);
/* 編集が必要なのはここまでです ! WordPress でブログをお楽しみください。 */
/** Absolute path to the WordPress directory. */
if (!defined('ABSPATH')) {
define('ABSPATH', dirname(__FILE__) . '/');
}
/** Sets up WordPress vars and included files. */
require_once(ABSPATH . 'wp-settings.php');wp-settings.php
コアファイル読み込み後、require_wp_db を実行しwpdbオブジェクトを生成するときにDB接続する。
/**
* @global wpdb $wpdb WordPress database abstraction object.
* @since 0.71
*/
global $wpdb;
// Include the wpdb class and, if present, a db.php database drop-in.
require_wp_db();
// Set the database table prefix and the format specifiers for database table columns.
$GLOBALS['table_prefix'] = $table_prefix;
wp_set_wpdb_vars();
// Start the WordPress object cache, or an external object cache if the drop-in is present.
wp_start_object_cache();
// Attach the default filters.
require ABSPATH . WPINC . '/default-filters.php';
// Initialize multisite if enabled.
if ( is_multisite() ) {
require ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-site-query.php';
require ABSPATH . WPINC . '/class-wp-network-query.php';
require ABSPATH . WPINC . '/ms-blogs.php';
require ABSPATH . WPINC . '/ms-settings.php';
} elseif ( ! defined( 'MULTISITE' ) ) {
define( 'MULTISITE', false );
}
register_shutdown_function( 'shutdown_action_hook' );
// Stop most of WordPress from being loaded if we just want the basics.
if ( SHORTINIT ) {
return false;
}wp();
WP()関数(WordPressリファレンス Developer Resources)
wp-includes/functions.phpで定義される関数。
WP $wp Current WordPress environment instance.
WP_Query $wp_query WordPress Query object.(メインクエりー)
WP_Query $wp_the_query 上記WordPress Query objectのコピー
処理 : $wpのmainメソッドを実行し$wp_queryにDBから取得したデータを設定。
/**
* Set up the WordPress query.
*
* @since 2.0.0
*
* @global WP $wp Current WordPress environment instance.
* @global WP_Query $wp_query WordPress Query object.
* @global WP_Query $wp_the_query Copy of the WordPress Query object.
*
* @param string|array $query_vars Default WP_Query arguments.
*/
function wp( $query_vars = '' ) {
global $wp, $wp_query, $wp_the_query;
$wp->main( $query_vars );
if ( ! isset( $wp_the_query ) ) {
$wp_the_query = $wp_query;
}
}$wp->main( $query_vars );
WP::main( string|array $query_args = '' )でWordPress 環境に必要なすべての変数を設定。
【参考】WP::main() (WordPressリファレンス Developer Resources)
main関数は、wp-includes/class-wp.php内で定義されている。
【main関数の処理】
$wp->parse_request
リクエストURL からクエリ変数配列へのデータ変形を行う。
$this->query_posts();クエリ変数配列から SQL 文が生成されデータベースへの問い合わせが行われる。/**
* Sets up all of the variables required by the WordPress environment.
*
* The action {@see 'wp'} has one parameter that references the WP object. It
* allows for accessing the properties and methods to further manipulate the
* object.
*
* @since 2.0.0
*
* @param string|array $query_args Passed to parse_request().
*/
public function main( $query_args = '' ) {
$this->init();
$parsed = $this->parse_request( $query_args );
$this->send_headers();
if ( $parsed ) {
$this->query_posts();
$this->handle_404();
$this->register_globals();
}template-loader.php
リクエストURLに基づいてテンプレートの読み込みが行われ、include $template;を実行し表示する。
wp-includes/template-loader.php
<?php
/**
* Loads the correct template based on the visitor's url
*
* @package WordPress
*/
if ( wp_using_themes() ) {
/**
* Fires before determining which template to load.
*
* @since 1.5.0
*/
do_action( 'template_redirect' );
}
/**
* Filters whether to allow 'HEAD' requests to generate content.
*
* Provides a significant performance bump by exiting before the page
* content loads for 'HEAD' requests. See #14348.
*
* @since 3.5.0
*
* @param bool $exit Whether to exit without generating any content for 'HEAD' requests. Default true.
*/
if ( 'HEAD' === $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] && apply_filters( 'exit_on_http_head', true ) ) {
exit;
}
// Process feeds and trackbacks even if not using themes.
if ( is_robots() ) {
/**
* Fired when the template loader determines a robots.txt request.
*
* @since 2.1.0
*/
do_action( 'do_robots' );
return;
} elseif ( is_favicon() ) {
/**
* Fired when the template loader determines a favicon.ico request.
*
* @since 5.4.0
*/
do_action( 'do_favicon' );
return;
} elseif ( is_feed() ) {
do_feed();
return;
} elseif ( is_trackback() ) {
require ABSPATH . 'wp-trackback.php';
return;
}
if ( wp_using_themes() ) {
$tag_templates = array(
'is_embed' => 'get_embed_template',
'is_404' => 'get_404_template',
'is_search' => 'get_search_template',
'is_front_page' => 'get_front_page_template',
'is_home' => 'get_home_template',
'is_privacy_policy' => 'get_privacy_policy_template',
'is_post_type_archive' => 'get_post_type_archive_template',
'is_tax' => 'get_taxonomy_template',
'is_attachment' => 'get_attachment_template',
'is_single' => 'get_single_template',
'is_page' => 'get_page_template',
'is_singular' => 'get_singular_template',
'is_category' => 'get_category_template',
'is_tag' => 'get_tag_template',
'is_author' => 'get_author_template',
'is_date' => 'get_date_template',
'is_archive' => 'get_archive_template',
);
$template = false;
// Loop through each of the template conditionals, and find the appropriate template file.
foreach ( $tag_templates as $tag => $template_getter ) {
if ( call_user_func( $tag ) ) {
$template = call_user_func( $template_getter );
}
if ( $template ) {
if ( 'is_attachment' === $tag ) {
remove_filter( 'the_content', 'prepend_attachment' );
}
break;
}
}
if ( ! $template ) {
$template = get_index_template();
}
/**
* Filters the path of the current template before including it.
*
* @since 3.0.0
*
* @param string $template The path of the template to include.
*/
$template = apply_filters( 'template_include', $template );
if ( $template ) {
include $template;
} elseif ( current_user_can( 'switch_themes' ) ) {
$theme = wp_get_theme();
if ( $theme->errors() ) {
wp_die( $theme->errors() );
}
}
return;
}
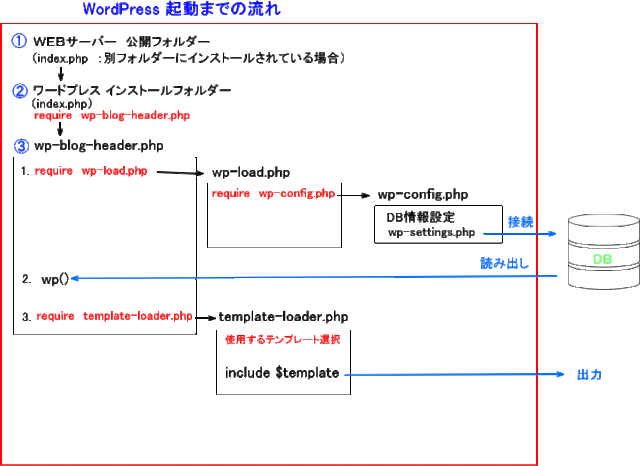
WordPress起動の流れまとめ
①apache 公開フォルダのindex.phpへ制御が渡る。
②wordpressインストールディレクトリのindex.phpへリダイレクトする。
(WordPressインストールが別フォルダーの場合)
③index.htm内でwp-blog-header.phpを呼び出す
3-1 wp-load.phpの呼び出し
3-1-1 wp-config.phpの呼び出し
3-1-2 wp-settings.phpの実行 → wp-config.php内の情報に基づいてDB接続。
3-2 wp()の呼び出し
3-2-1 WP::main() → URLに基づいてデーターベースへSQL文を発行しDBを読み込む。
3-3 template-loader.php → do_action( 'template_redirect' )で使用するテンプレートを決定しinclude $template;でHTMLを表示。